147 Insertion Sort List
Sort List
문제
Given the head of a singly linked list, sort the list using insertion sort, and return the sorted list’s head.
The steps of the insertion sort algorithm:
- Insertion sort iterates, consuming one input element each repetition and growing a sorted output list.
- At each iteration, insertion sort removes one element from the input data, finds the location it belongs within the sorted list and inserts it there.
- It repeats until no input elements remain.
The following is a graphical example of the insertion sort algorithm.
The partially sorted list (black) initially contains only the first element in the list.
One element (red) is removed from the input data and inserted in-place into the sorted list with each iteration.
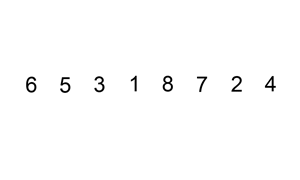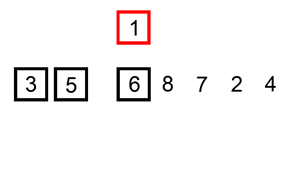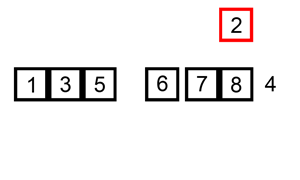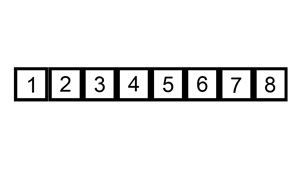
조건
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range [1, 5000].
- -5000 $\le$ Node.val $\le$ 5000
예제
Input: head = [4,2,1,3]
Output: [1,2,3,4]
Input: head = [-1,5,3,4,0]
Output: [-1,0,3,4,5]
해결
1st
1 생각
- 순차적으로 계속 위치를 찾아야 하므로 중첩 반복문 필요
정렬을 해야 하는 값을 기준으로,정렬된 값들과 비교하면서 노드를 변경- 파이썬에서 객체를 변수에 할당 시 참조 주소가 할당 됨에 주의
1 코드
def insertionSortList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
"""
1. Insertion sort iterates, consuming one input element each repetition and growing a sorted output list.
2. At each iteration, insertion sort removes one element from the input data, finds the location it belongs within the sorted list and inserts it there.
3. It repeats until no input elements remain.
"""
ans = parent = ListNode(0)
# head: 정렬하려는 값
while head:
# head가 들어가야 하는 위치를 찾는다
while ans.next and ans.next.val < head.val:
ans = ans.next
# p.211 다중 할당
# ans.next, head.next, head = head, ans.next, head.next
# 다중 할당은 아래와 같이 바꿀 수 있다
tmp_ans_next = ans.next
tmp_head_next = head.next
# head(3)가 ans(2) 다음값이 되고
# 2 -> 4
# 2 -> 3
ans.next = head
# 기존 ans의 다음 값(4)은 다다음 값이 된다
# 2 -> 3 -> 4
ans.next.next = tmp_ans_next
# 그리고 앞서 미리 저장해둔 다음 head의 next 값을 head로 치환
head = tmp_head_next
# 매번 ans를 처음부터 탐색할 수 있도록 한다
# ans = parent
# [개선]
# 다음에 정렬시켜야 하는 head의 값이 현재 ans값보다 크거나 같다면,
# 굳이 처음부터 다시 탐색할 필요가 없이 계속 뒤에 붙여 나가면 된다
if head and ans.val > head.val:
# 현재 ans 값보다 다음에 정렬시켜야 하는 head의 값이 작다면,
# 그 작은 값이 위치할 곳을 찾아야 하므로 처음부터 다시 탐색한다
ans = parent
# return ans.next
# [개선]
return parent.next
1 결과
19 / 19 test cases passed.
Status: Accepted
Runtime: 168 ms
Memory Usage: 16.2 MB